Welcome to the Sea Level Tracker!
- Show actual sea level vs. the projected sea level change curves plainly and
- Answer the question, "What rate of sea level change is currently being observed at the selected gauge?"
There are five main sections to the Sea Level Tracker:
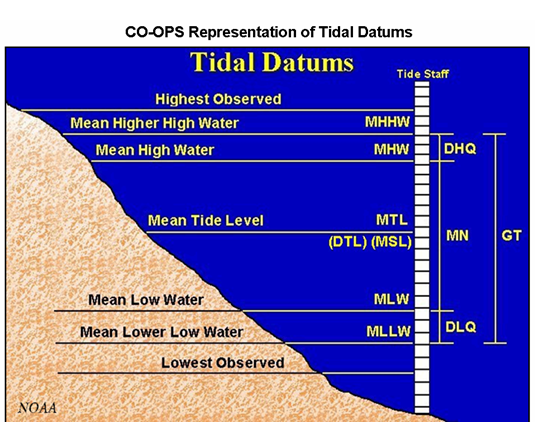
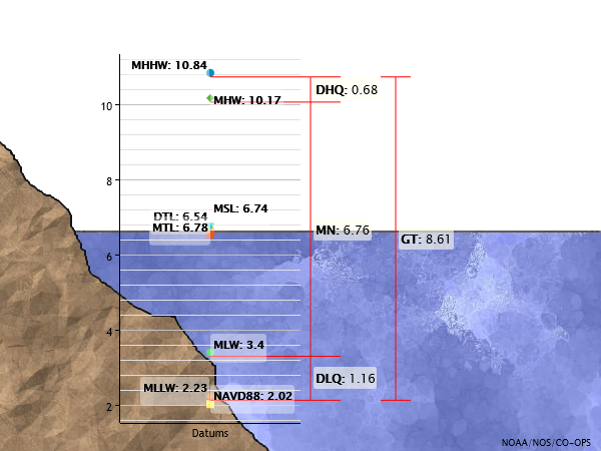
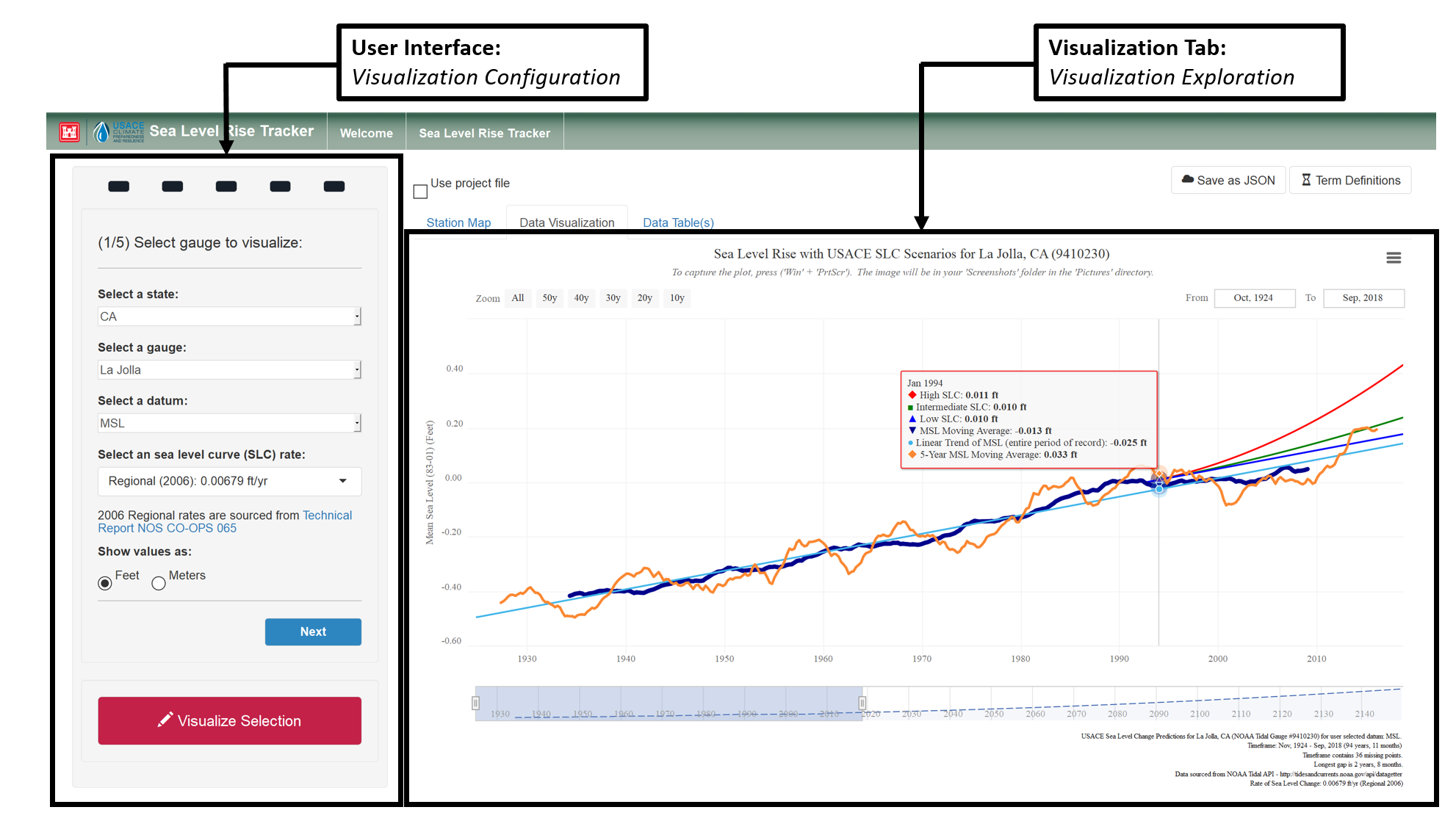
- Data Entry Panel: Here, the user selects the location and gauge to be analyzed, configuring the visualization characteristics. This includes the gauge, measurement datum, sea level curve rates, various smoothing curves of historical data, trend lines, extreme water levels, and critical elevations for comparison.
- Location Map: The map shows the geographic location of the selected gauge. The Sea Level Tracker also allows the user to select the desired gauge for analysis from the map. Just click the location of interest, marked with blue icons.
- Visualization Tab: The generated visualization captures the historic hydrologic behavior for the user-selected location, while taking into account historic trends in sea level rise. The final output is configured by the user's selections in the User Interface.
- Feasibility Study Report: This tab allows users to generate a downloadable report that contains the key outputs from the Sea Level Tracker as well as the inputs used to create them.
- Data Table(s) Tab: For deeper inspection, the Sea Level Tracker allows the user to explore the raw data. The tool allows for variable selection above the table, while also letting the user filter the selected variables to ranges of interest.
Please acknowledge the US Army Corps of Engineers for producing this tool and making it freely available as part of their progress in climate preparedness and resilience.
Sea Level Tracker - Data Source(s):
Data used in calculations for Sea Level Change are pulled from the NOAA Center for Operational Oceanographic Products and Services Application Programming Interface (CO-OPS API). The CO-OPS Data API is a flexible retrieval mechanism for direct access to CO-OPS' products, such as water levels, predictions, currents, meteorological observations, and more. Users can retrieve output in multiple common formats. The CO-OPS Metadata API can be used to retrieve information about CO-OPS' stations. A request can be made to return information about a specific station, or information about multiple stations can be returned. The types of information accessible via the API are listed in detail under Resource Types. Information on how to use to query data through the CO-OPS API can be found here.
Note: The tool does not predict future water levels. Rather, the tool offers smoothed analysis of historic sea level behavior and the measured trends at a user selected gauge.
To learn more about the tool, we strongly recommend reading the user guide (PDF version available here).